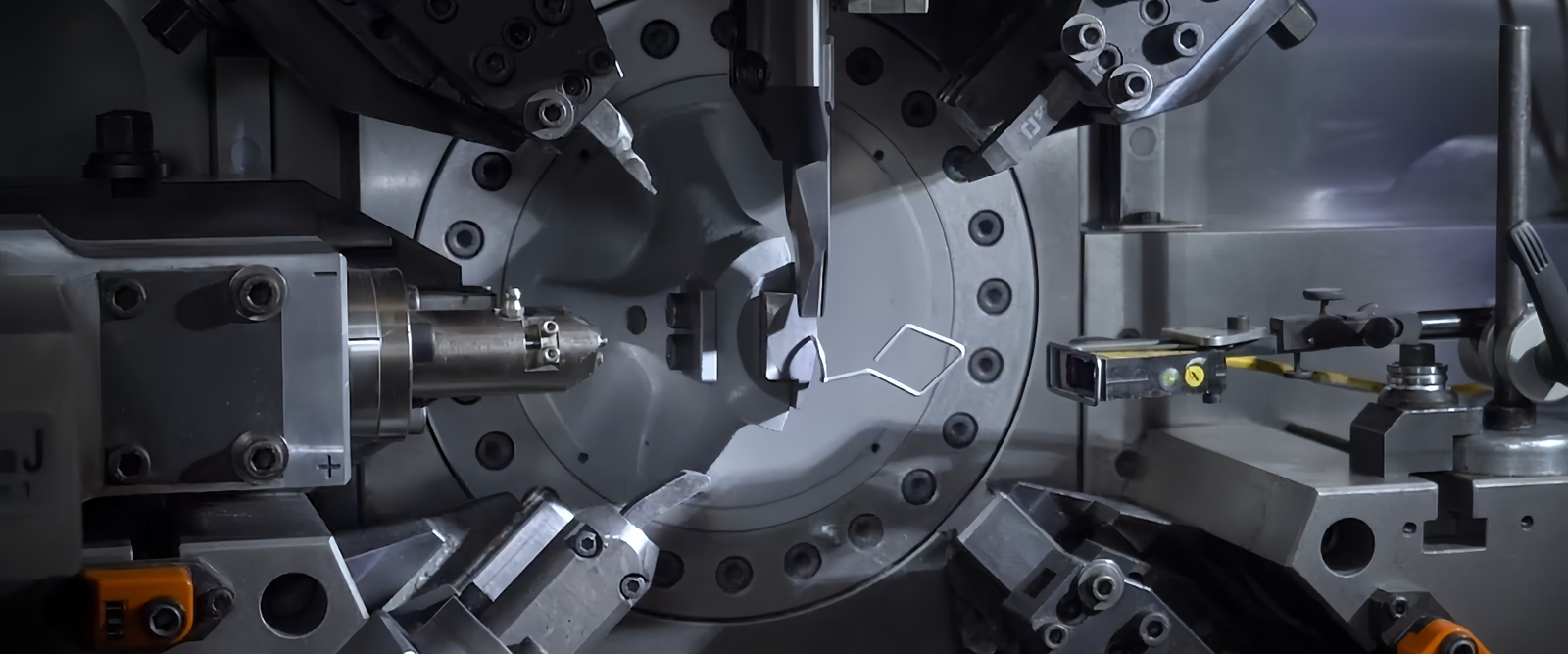
– Drive Components for Medical Forceps: Precisely Transmitting Every Surgical Intent
We provide high-precision, high-reliability springs and linkage components for all types of biopsy forceps, endoscopic forceps, and minimally invasive surgical forceps, ensuring every actuation of the jaw is precise, sharp, and reliable.
Medical Forceps Technology Overview: The Surgeon’s Extended Sense of Touch
From biopsy forceps that retrieve pathological samples to surgical forceps that perform delicate maneuvers in laparoscopic surgery, medical forceps are among the surgeon’s most vital tools. Their core functions—grasping, dissecting, cutting—rely on a drive system that can accurately transmit the surgeon’s hand movements to the distal jaws. The heart of this system is often composed of precision springs, pull rods, and linkage mechanisms. Here, the spring not only provides the power for opening and closing but also critically influences the operational “feel” and force feedback the surgeon receives.
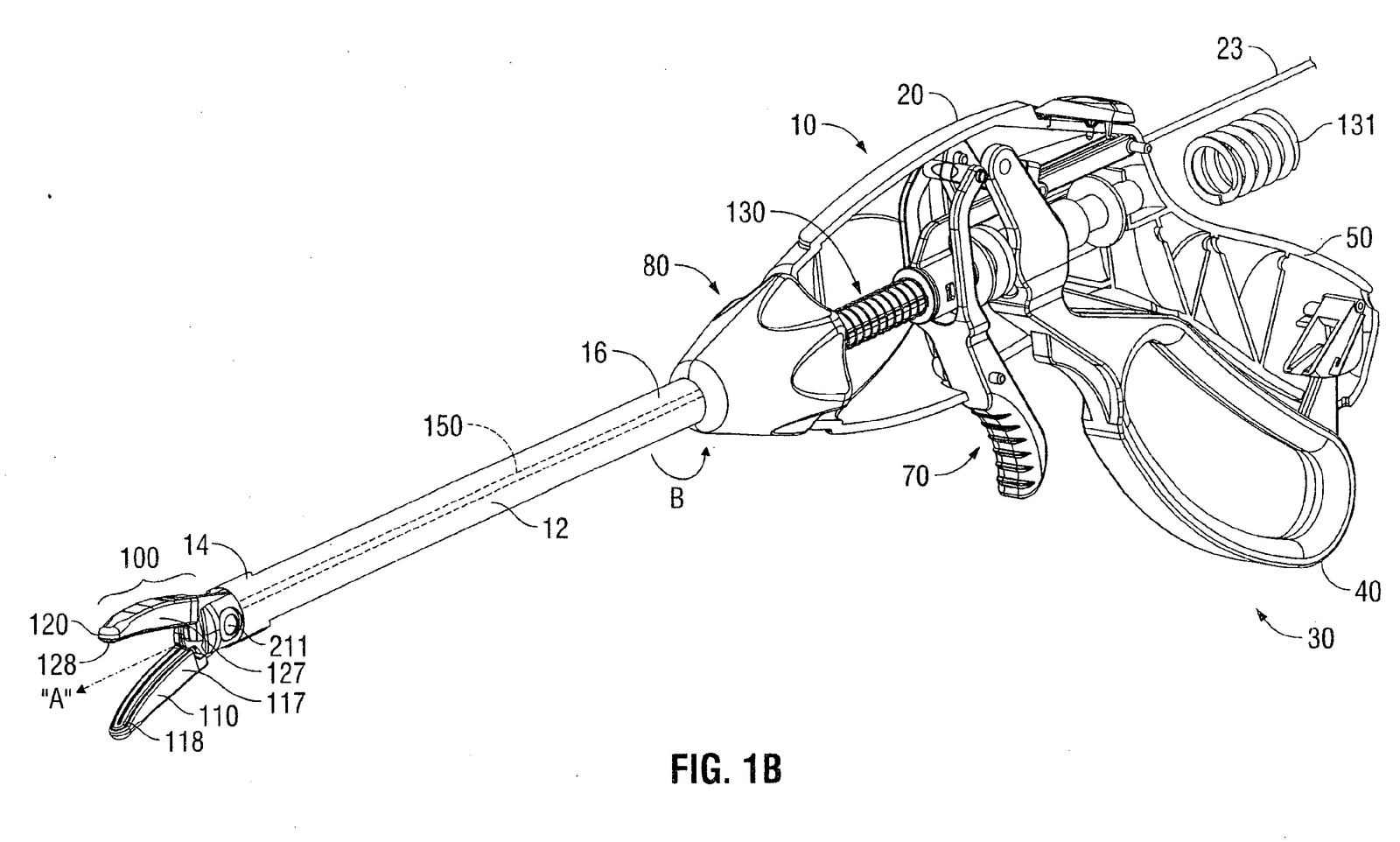
FIG. 1B is a side, perspective view of the endoscopic bipolar forceps illustrating internal components of a handle assembly associated with the endoscopic bipolar forceps. With reference to FIGS. 1B, The drive assembly 130 is in operative communication with handle assembly 30 for imparting movement of one or both of a pair of jaw members 110, 120 of end effector assembly 100. Conventional drive assemblies typically utilize one or more types of springs, e.g., a compression spring, to facilitate closing the jaw members 110 and 120.
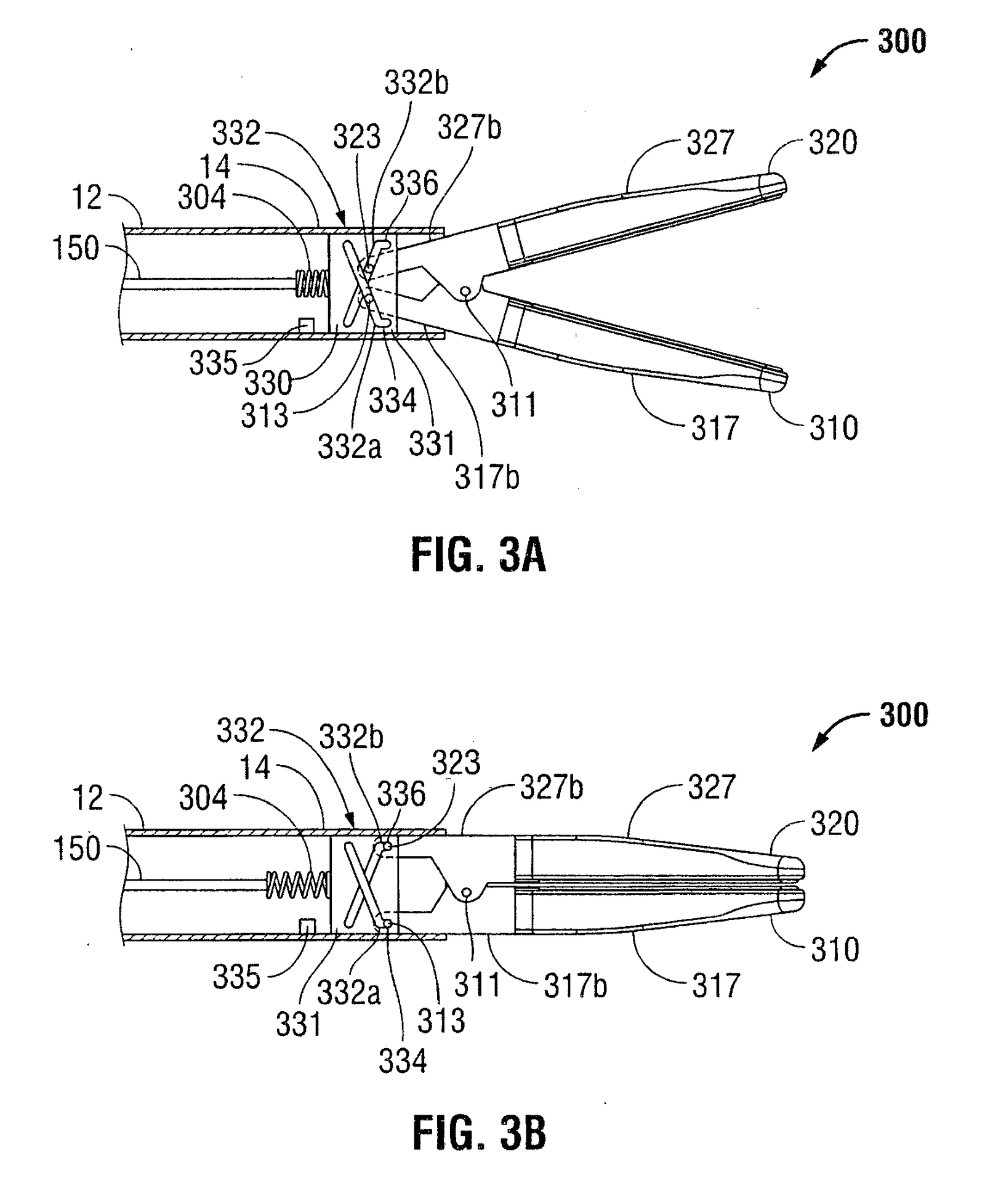
FIGS. 3A and 3B are schematic views of jaw members operably coupled to a distal end of the endoscopic forceps depicted in FIGS. 1B according to an embodiment of an end effector 300 that is configured for use with the forceps 10 is illustrated. End effector 300 is substantially identical to end effector 100.
One or more types of resilient members 304 operably couple to the drive element 150 and to the cam assembly 330. Resilient member 304 may be any suitable resilient member, e.g., a compression spring. A distal end of the drive element 150 operably couples to a proximal end of the resilient member 304 and proximal end of the cam assembly 330 operably couples to a distal end of the resilient member 304. The resilient member 304 operably couples to the distal end of the drive element 150 and proximal end of the cam assembly 330 via any suitable coupling methods. As described above with resilient member 204, resilient member 304 cooperates with the drive assembly 130 to provide the necessary closure force on the jaw members 310 and 320 for sealing tissue.
We specialize in the core of the forceps drive system, understanding that a reliable spring component is paramount to surgical success and patient safety.
Medical Forceps Component Solutions
Biopsy Forceps
- Challenge: The jaws must be sharp enough to obtain a complete tissue sample, while the drive system must ensure smooth actuation without jamming.
- Our Solution: We provide high-cleanliness micro compression or extension springs that ensure rapid jaw reset during operation. We can optimize the spring’s force-deflection curve to provide the surgeon with clear haptic feedback.
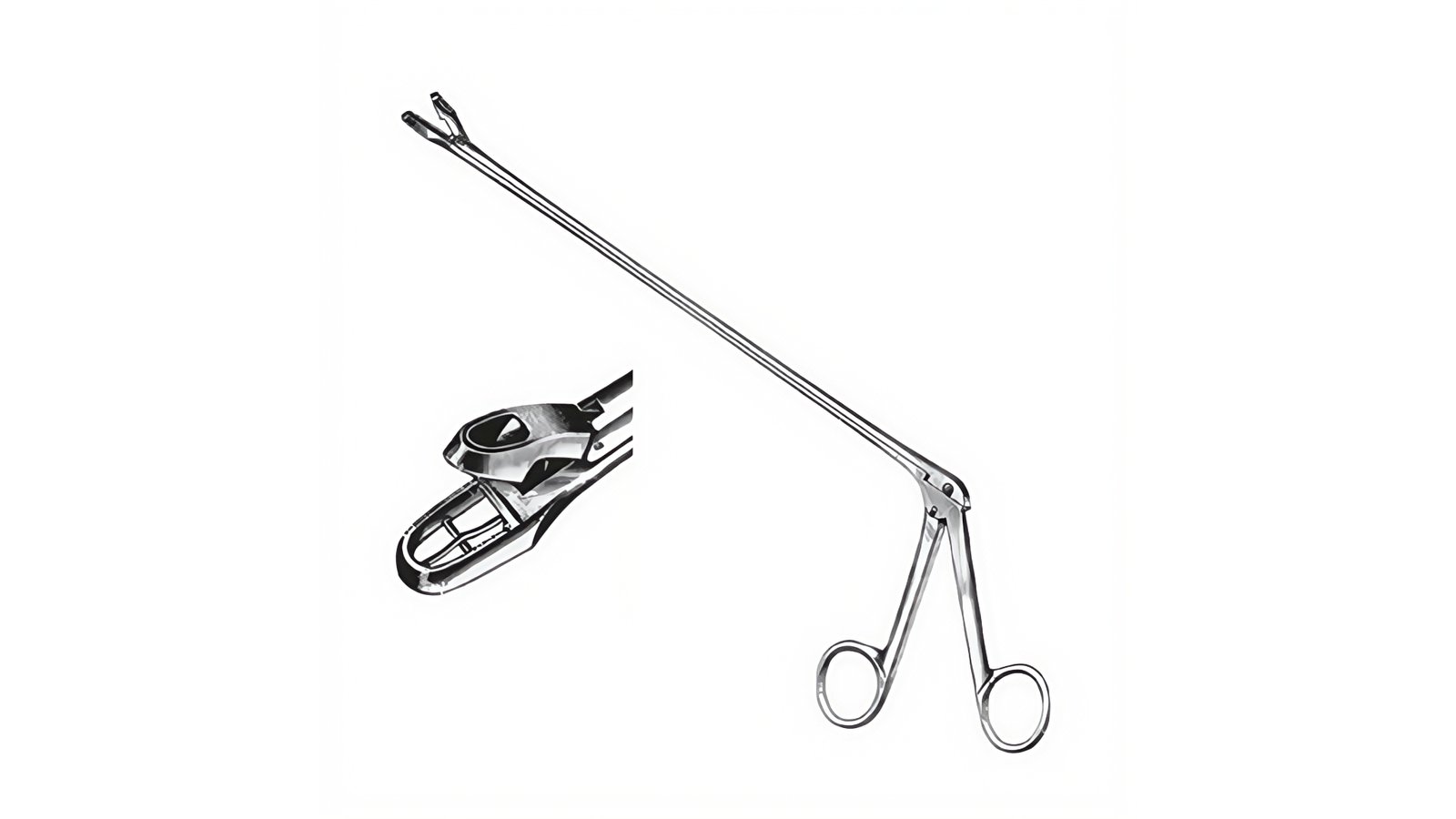

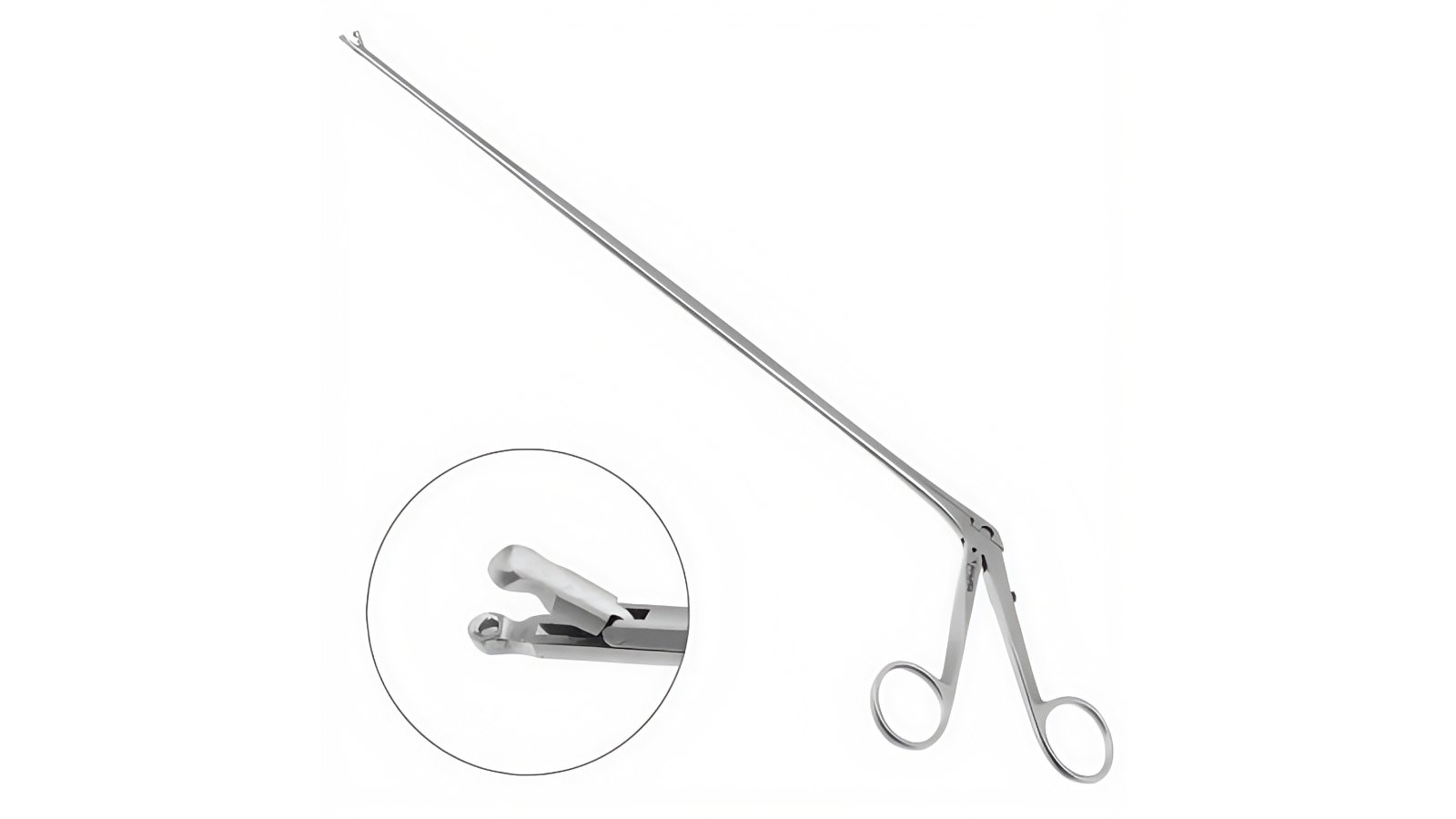
Endoscopic Forceps
- Challenge: Within long, flexible endoscope channels, drive force must be transmitted efficiently, and components must be corrosion-resistant and easily sterilizable.
- Our Solution: We use high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials like 316LVM or 17-7PH stainless steel for springs and pull wires. Our compact designs ensure maximum performance in limited spaces.
Vascular Clamp Forceps
- Challenge: Require a precise and stable clamping force that can occlude a vessel without causing permanent damage.
- Our Solution: We design custom flat springs (leaf springs) or wire forms with specific mechanical properties. Through rigorous mechanical testing, we ensure high consistency in clamping force from batch to batch.
Minimally Invasive Surgical (MIS) Forceps
- Challenge: Involve complex drive mechanisms that demand high integration, lightweight design, and the ability to withstand repeated high-pressure steam sterilization.
- Our Solution: We provide custom spring and linkage components made from high-performance alloys like MP35N®, which maintain their mechanical properties even under harsh sterilization conditions.
Technical Specifications & Capabilities
| Parameter | Specification & Capability |
| Materials | 17-7PH / 304 Stainless Steel, MP35N® |
| Core Processes | Precision Spring Coiling, Wire Forming, Stamping, Laser Welding, 100% Force Testing |
| Wire Diameter | 0.1mm – 0.8mm (0.004″ – 0.031″) |
| Outer Diameter | 0.5mm – 5.0mm (0.020″ – 0.197″) |
| Load Capacity | Custom designed from grams to kilograms of force |
| Cycle Life | Can be designed and fatigue-tested to meet specific requirements |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Compatible with EtO, Autoclave (Steam), Gamma, and other methods |
Core Performance Advantages
High Reliability & Durability
Components are designed to withstand thousands of actuation cycles and repeated sterilization without performance degradation.
Precise Force Transmission
Optimized designs ensure minimal loss of force from the handle to the jaws.
Consistent Performance
Strict process controls guarantee high batch-to-batch consistency in product performance.
Excellent Biocompatibility
Use of medical-grade materials compliant with stringent FDA and MDR requirements.
.png)